The progress that has been made in the treatment of small cell lung cancer has resulted from improved development of multi modality treatments and participation in clinical trials.
Recurrent non small cell lung cancer prognosis.
Prognosis following recurrence subsequent to complete resection of non small cell lung cancer nsclc is considered a multifactorial process dependent on clinicopathological biological and treatment characteristics.
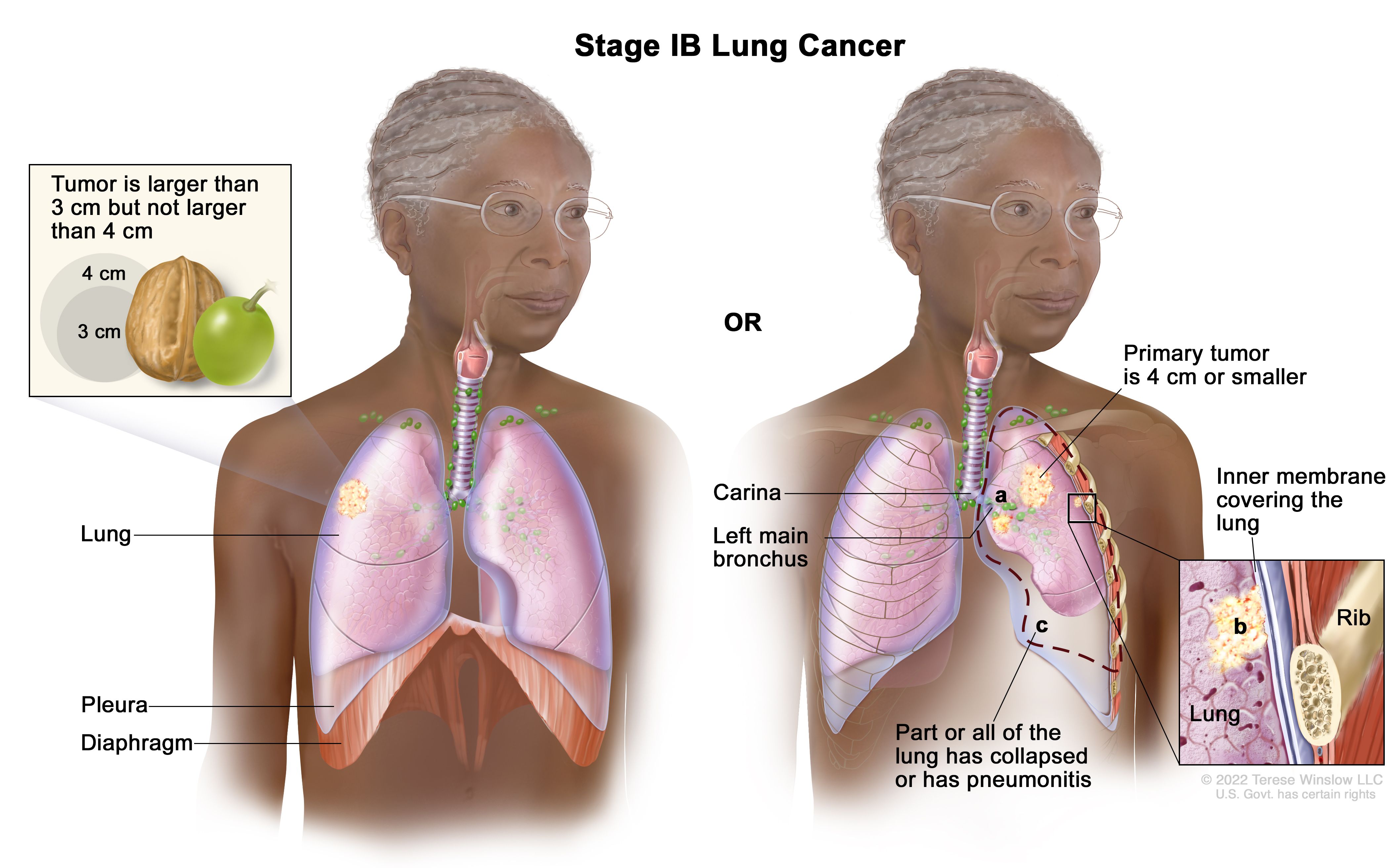
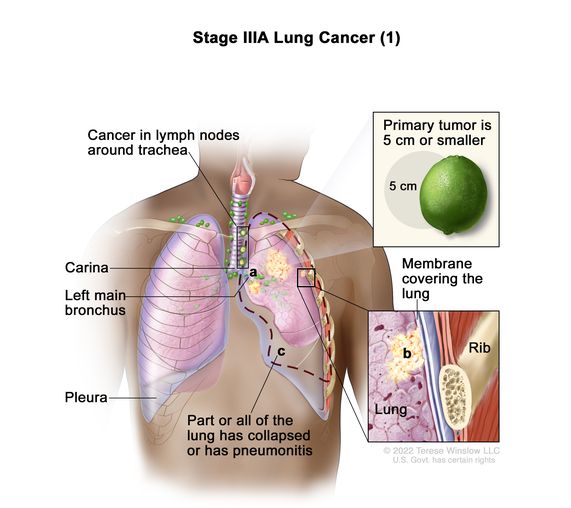
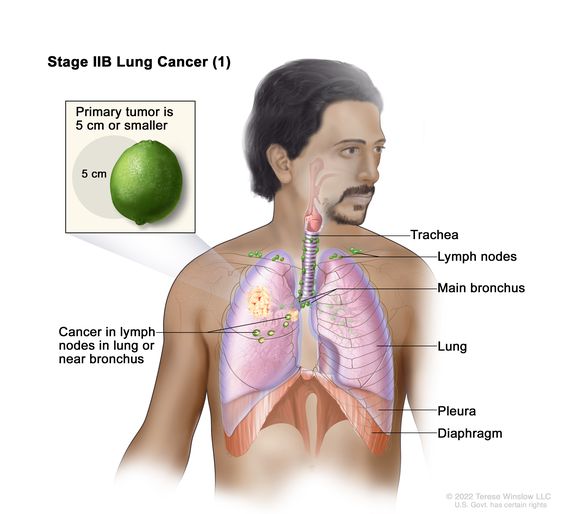
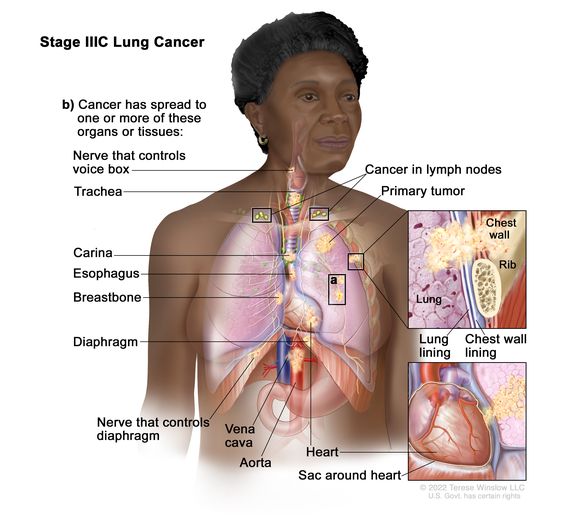
The risk of recurrence varies by the stage of cancer of which nsclc has five stage 0 through stage 4.
Gefitinib was approved for lung cancer treatment in japan in 2002.
This is a dangerous disease that can cause breathing difficulties and.
Prognosis following recurrence subsequent to complete resection of non small cell lung cancer nsclc is considered a multifactorial process dependent on clinicopathological biological and treatment characteristics.
Gefitinib was approved for lung cancer treatment in japan in 2002.
The national cancer institute s database breaks down the cancers by how far the tumors.
Among people with non small cell lung cancer nsclc the most common form of the disease between 30 and 55 will experience recurrence.
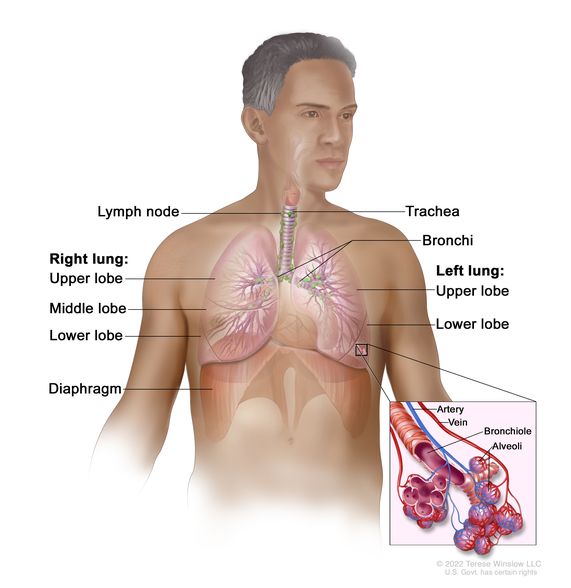
Non small cell lung carcinoma is a type of lung cancer also commonly referred to as non small cell lung cancer nsclc.
Relapse of stage i small cell lung cancer ten or more years after the.
Around three in 10 people will experience relapse with stage 1.
Non small cell lung cancer.
Non small cell lung cancer grows and spreads slower than small cell lung cancer.
Patients experiencing a recurrence of nsclc historically have had few treatment options.
The aim of the c.
When non small cell lung cancer nsclc has progressed or returned following an initial treatment with surgery radiation therapy and or chemotherapy it is said to be recurrent or relapsed.
While progress has been made in the treatment of small cell lung cancer better treatment strategies are needed as many patients still experience disease recurrence.
Treatment for recurrent non small cell lung cancer japanese journal of clinical oncology.

/non-small-cell-lung-cancer-symptoms-4588803_final_CORRECTED-bb05e218504e4d3788bd7e5a2d99d3a7.png)